서로 다른 상태를 지닌 여러 인스턴스를 사용하여 경주하는 거북이를 만들어보겠다.
1. 화면 창을 키우기
setup(width, height)
이 경우 위치인수보다는 키워드인수를 사용하면
코드가 더 명확해진다.

2. 글자/숫자 입력하기
textinput(title, prompt)
문자열 입력을 위한 대화 상자 창읠 띄운다.
title은 대화 창의 제목이고, prompt는 어떤 정보를 입력해야 하는지 설명하는 텍스트이다.
numinput(title, prompt, minval=None, maxval=None)
숫자 입력을 위한 대화 상자 창을 띄운다.
파라미터 중 minval은 입력의 최솟값, maxval은 입력의 최댓값을 뜻한다.

<코드>
from turtle import Turtle, Screen
nin = Turtle()
screen = Screen()
# 화면 크기 조절
screen.setup(height=400, width=400)
# 화면창 띄우기
screen.textinput(title="winner", prompt="Who's winner?")
screen.exitonclick()<실행화면>

3. 시작 자리로 거북이 이동시키기
좌표계를 이해하도록 해보자.
거북이가 처음에 있는 자리가 (0,0)이라고 한다면

x축의 오른쪽 방향으로 가면 +, 왼쪽은 -
y축의 위쪽 방향으로 가면+, 아래쪽은 -이다.

게임 시작 전에
거북이를 빨강, 초록, 노랑, 파랑이 있는 자리로 옮겨야 한다.

빨강 거북이 좌표를 대강 계산해보자.

(-180, 180) 위치로 거북이를 이동시키기 위해
goto(x, y) 메소드를 쓴다.
x,y의 좌표로 이동시켜라는 뜻이다.
nin.goto(x=-180, y=180)
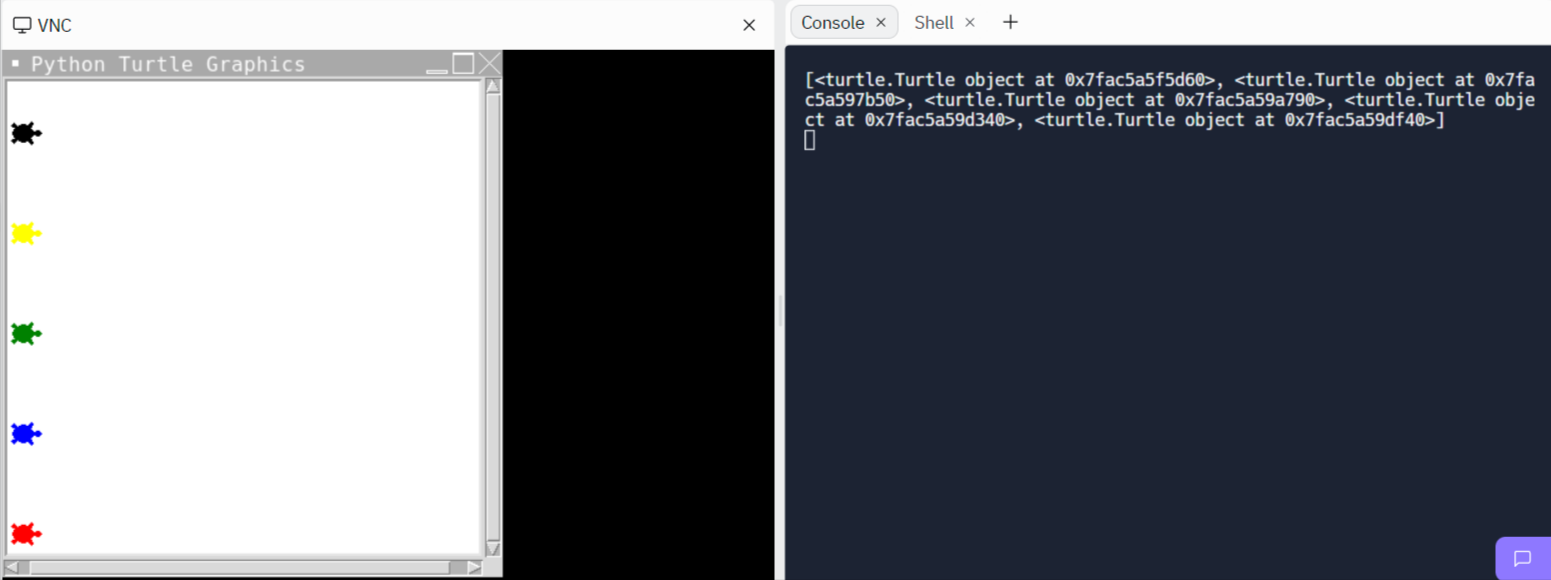
<코드>
turtle_list =[]
color_list = ["red", "blue", "green", "yellow", "black"]
for i in range(0,5):
name = Turtle(shape="turtle")
name.color(color_list[i])
name.penup()
name.goto(x=-180, y = (-170+ i*80))
turtle_list.append(name)
print(turtle_list)<실행창>
4. 달리기 시작하기
for turtle in turtle_list:
step = random.randint(1,10)
turtle.forward(step)
5. 게임 종료하기
하나의 거북이가 결승점에 도달하면 이긴다.
그때의 거북이의 x좌표를 구해보자.
화면의 x좌표의 오른쪽 끝은 200이다.
하지만, 거북이가 결승점에 닿을 때 x좌표는 200이 아니다.
거북이의 폭을 고려해야 하기 때문이다.
거북이의 크기(40,40) 에서 x길이의 절반 만큼을 빼줘야 한다.
즉
200-(40/2) = 180이다.

xcor(), ycor()
거북이의 현재 x좌표, 현재 y좌표를 알 수 있다.

<코드>
keep_going = True
while keep_going:
for turtle in turtle_list:
if turtle.xcor() >180:
keep_going= False
winner = turtle.pencolor()
if winner == user:
print(f"You've won! {winner} is the winner!")
else:
print(f"You've lost! {winner} is the winner!")
else:
for turtle in turtle_list:
step = random.randint(1,10)
turtle.forward(step)

<최종 코드>
from turtle import Turtle, Screen
import random
screen = Screen()
screen.setup(height=400, width=400)
user = screen.textinput(title="winner", prompt="Who will be winner?")
print(user)
turtle_list =[]
color_list = ["red", "blue", "green", "yellow", "black"]
for i in range(0,5):
name = Turtle(shape="turtle")
name.color(color_list[i])
name.penup()
name.goto(x=-180, y = (-170+ i*80))
turtle_list.append(name)
# print(turtle_list[0].shapesize())
keep_going = True
while keep_going:
for turtle in turtle_list:
if turtle.xcor() >180:
keep_going= False
winner = turtle.pencolor()
if winner == user:
print(f"You've won! {winner} is the winner!")
else:
print(f"You've lost! {winner} is the winner!")
else:
for turtle in turtle_list:
step = random.randint(1,10)
turtle.forward(step)
screen.exitonclick()'파이썬 > 파이썬(python) 중급' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [20-2 파이썬] 뱀 게임 만들기 2(클래스 만들기) (2) | 2022.08.28 |
|---|---|
| [20-1 파이썬] 뱀 게임 만들기 1(터틀 명령어 재밌게 공부하기) bgcolor(), title(),shape(), xcor(), ycor(),set(x), set(y), goto(x,y), penup(), pendown(), forward(), backward(), tracer(), update() (0) | 2022.08.28 |
| [19-5 파이썬] 터틀 방향 & 각도 숫자 의미(0, 90, 270, 360) (0) | 2022.08.27 |
| [19-4 파이썬] 인스턴스(instance), 상태(state) (0) | 2022.08.27 |
| [19-3 파이썬] 드로잉팬 만들기(터틀 명령어 실습) (0) | 2022.08.27 |