목차
1. 라이브러리
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import pickle as pkl
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, PredefinedSplit, GridSearchCV
from sklearn.metrics import f1_score, precision_score, recall_score, accuracy_score
2. 데이터
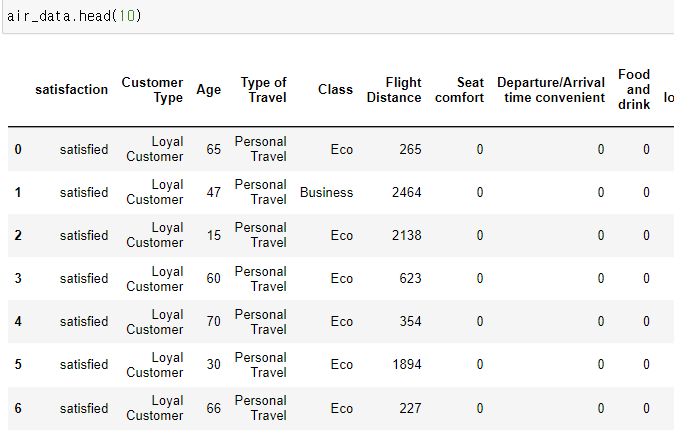
3. null값처리
air_data_subset = air_data.dropna(axis=0)
4. Encoding
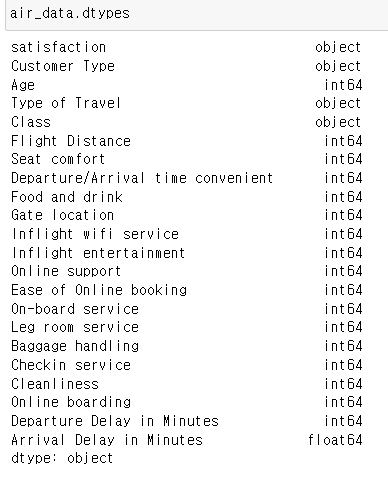
air_data_subset_dummies = pd.get_dummies(air_data_subset,
columns=['Customer Type','Type of Travel','Class'])
5. 데이터분할
# X, y값 정하기
y = air_data_subset_dummies["satisfaction"]
X = air_data_subset_dummies.drop("satisfaction", axis=1)
# 데이터분할
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.25, random_state = 0)
X_tr, X_val, y_tr, y_val = train_test_split(X_train, y_train, test_size = 0.25, random_state = 0)
7. 모델 튜닝
1) 하이퍼파라미터
cv_params = {'n_estimators' : [50,100],
'max_depth' : [10,50],
'min_samples_leaf' : [0.5,1],
'min_samples_split' : [0.001, 0.01],
'max_features' : ["sqrt"],
'max_samples' : [.5,.9]}
2) 데이터 인덱스 분할
split_index: X_trian 데이터에서, X_tr과 X_val 셋을 구분하여 인덱스를 생성한다.
custom_split: split index를 PredefinedSplit에 넣는다. PredefinedSplit는 사이킷런에서 제공하는 분할전략이다. 이를 사용하면 머신러닝모델을 교차검증할 때 직접 분할 인덱스를 정할 수 있다. 즉, 훈련세트와 검증세트의 분할을 미리 정의하고, 이를 활용하여 교차 검증을 수행할 수 있다.
split_index = [0 if x in X_val.index else -1 for x in X_train.index]
custom_split = PredefinedSplit(split_index)
3) 랜덤포레스트 모델 만들기
rf= RandomForestClassifier(random_state=0)
4) GridSearch 모델로 하이퍼파라미터튜닝
GridSearchCV로 랜덤포레스트 모델의 하이퍼파라미터 튜닝을 수행하는 코드이다.
cv: 교차검증전략
refit: 최적의 하이퍼파라미터 조합을 찾은 후 해당 조합으로 모델을 다시 학습시켜 사용할 평가 지표.
n_jobs: 사용할 CPU 코어 개수, -1은 가능한 모든 코어 이용하겠다.
verbose: 진행 상황 출력할지 여부, 1은 자세히 하겠다.
rf_val = GridSearchCV(rf, cv_params, cv=custom_split, refit='f1', n_jobs = -1, verbose = 1)
5) 학습
rf_val.fit(X_train, y_train)
6) 최적의 파라미터
rf_val.best_params_{'max_depth': 50,
'max_features': 'sqrt',
'max_samples': 0.9,
'min_samples_leaf': 1,
'min_samples_split': 0.001,
'n_estimators': 50}
7) 모델 설계 및 학습
rf_opt = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators = 50, max_depth = 50,
min_samples_leaf = 1, min_samples_split = 0.001,
max_features="sqrt", max_samples = 0.9, random_state = 0)
rf_opt.fit(X_train, y_train)
8) 평가
# 예측값
y_pred = rf_opt.predict(X_test)
# score
pc_test = precision_score(y_test, y_pred, pos_label = "satisfied")
ac_test = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
ac_test = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
f1_test = f1_score(y_test, y_pred, pos_label = "satisfied")
print("\nThe precision score is: {pc:.3f}".format(pc = pc_test), "for the test set,", "\nwhich means of all positive predictions,", "{pc_pct:.1f}% prediction are true positive.".format(pc_pct = pc_test * 100))The precision score is: 0.950 for the test set,
which means of all positive predictions, 95.0% prediction are true positive.
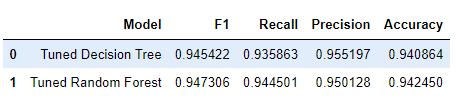
9) 모델 평가
# Create table of results.
### YOUR CODE HERE ###
table = pd.DataFrame()
table = table.append({'Model': "Tuned Decision Tree",
'F1': 0.945422,
'Recall': 0.935863,
'Precision': 0.955197,
'Accuracy': 0.940864
},
ignore_index=True
)
table = table.append({'Model': "Tuned Random Forest",
'F1': f1_test,
'Recall': rc_test,
'Precision': pc_test,
'Accuracy': ac_test
},
ignore_index=True
)
table